Atmospheric green house effect
by N.Pavan kumar
(Kavali,Andrapradesh,India.)
See the heating of the planet's surface arising from the blanketing effect of anthropogenic carbon dioxide in the air.
What gases? carbon-dioxide, Nitrous oxide, Methane and Chloro flurocarbons. We know most about carbon dioxide because it gets the most publicity. Take note that Ozone and sulphur dioxide act as serious pollutants and may contribute to global warming as well.
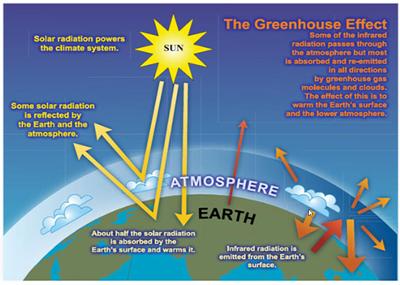
Barry's Response - Earth's climate is driven by energy from the sun. A lot of that radiation bounces off the earth or the air and clouds above. Almost half of the energy stays here and warms up the planet's surface. Our earth has to let the heat out eventually.
How does the atmospheric green house effect work? Blackbody infrared radiation tries to escape heat. Some of the energy passes through the air, some is absorbed and transmitted upward and downward. It happens all the time.
The greenhouse effect increases when the atmosphere gets better at absorbing and stopping the outgoing heat, so the atmosphere stays warmer. Even at the "new level" (higher global temperatures), the earth loses the same amount of heat as it gains. Scientists call that an equilibrium. As the absorption characteristics in the atmosphere change, higher global temperatures are needed to keep heat-flow equilibrium by producing the right mix of emitted radiation wavelengths.
Search this site for more information now.
Let's simplify it and explain it in an easy-to-understand manner
We all need to be aware of how we use energy and take care of our planet. All of us can help keep our planet a healthy and comfortable place to live by using cleaner and greener energy sources, planting trees, and reducing waste. So now that brings up climate change. A big reason the Earth is getting warmer is the "blanketing effect" caused by certain gases in the air.
Think of the Earth as a cozy house, and the atmosphere as a blanket. We keep warm with this blanket because it traps some of the sun's heat. We've been adding extra "blankets" to the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide, methane, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
CO2 is like the star in this story because it gets all the attention. Carbon dioxide comes from burning fossil fuels (like oil and gas) and cutting down trees. Our "blanket" gets thicker when we use cars, factories, and machines.
Methane and nitrous oxide are also bad. Cow burps (yes, really!) and old landfills release methane. Fertilizers produce nitrous oxide. CO2 isn't the only gas that contributes to global warming, but these gases do as well.
CFCs, on the other hand, were used in refrigerators and aerosol sprays. Even though they're not used much anymore, they're powerful blanket makers. Now let's talk about two other pollutants that contribute to warming: ozone and sulfur dioxide. High up in the atmosphere, ozone protects us from the sun's harmful rays. Where we live, it's a problem because it traps heat like a mini-blanket.
The main source of sulfur dioxide is burning dirty fuels like coal and sour gas in flares. In combination with other pollutants, it can make clouds that reflect the sun's heat back into space, but it can also warm the Earth.
Last but not least, water vapor! In the atmosphere, it acts like a "natural blanket." This "natural blanket" gets thicker as the Earth gets warmer.
Extra "blankets" and "mini-blankets" make the Earth warmer than it should be, like when you wear too many sweaters. We could see big changes in our climate, like melting ice, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather.
Comments for Atmospheric green house effect
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Do you have concerns about air pollution in your area??
Perhaps modelling air pollution will provide the answers to your question.
That is what I do on a full-time basis. Find out if it is necessary for your project.
Have your Say...
on the StuffintheAir facebook page
Other topics listed in these guides:
The Stuff-in-the-Air Site Map
And,
Thank you to my research and writing assistants, ChatGPT and WordTune, as well as Wombo and others for the images.
OpenAI's large-scale language generation model (and others provided by Google and Meta), helped generate this text. As soon as draft language is generated, the author reviews, edits, and revises it to their own liking and is responsible for the content.