- Air Homepage
- Weather Equipment
- Barometer Makes
Many types of barometer makes for measuring air pressure.
Learn more about weather instruments.
A barometer makes atmospheric pressure measurements.
The pressure tries to flatten you with the weight of several miles of air above you - YES, AIR DOES WEIGH SOMETHING.
How much? Think of a vertical box on Long Island, 1 foot square (not very big) going up to the top of the atmosphere. There would be over 2000 pounds of downward force in that box.
In simple terms, air pressure is how much weight the Earth's atmosphere exerts on anything inside it. It's an essential part of meteorology, weather forecasting, and many other fields of science and engineering to measure air pressure.
Changes in air pressure are critical in determining weather patterns, and meteorologists closely monitor pressure trends to forecast weather events and help people prepare. More on this below.
There are several types of barometers available to fit different applications and needs, and they're important tools for measuring air pressure.
Why atmospheric pressure? Barometric pressure plays a big role in weather forecasting. Barometric pressure changes indicate changes in atmospheric conditions, which can help predict weather patterns. People can make informed decisions about outdoor activities, travel plans, and weather-related precautions by monitoring barometric pressure trends.
People with certain health conditions may be sensitive to changes in barometric pressure. Shifts in atmospheric pressure can affect migraines, arthritis, or sinus problems. Keeping an eye on the barometric pressure can help them manage their health.
Barometric pressure can affect outdoor activities. Fishermen, for instance, pay attention to barometric pressure since it affects fish behavior. Hikers, mountaineers, and pilots may consider changes in barometric pressure for altitude adjustments, weather changes at higher elevations, or flight planning.
The barometric pressure has been historically important in meteorology, aviation, and scientific research. Folk wisdom connects barometric pressure changes to weather lore and predicting rain, storms, and fair weather.
Personal curiosity: Some people are fascinated by the atmosphere and weather phenomena and enjoy monitoring barometric pressure. They might enjoy watching how barometric pressure changes over time and how it affects weather.
What's the deal with barometers?
Air pressure (also known as atmospheric pressure) is measured by barometers. This force is exerted by the air above a point. In meteorology, barometers can tell you how the weather's doing, thus making them essential tools. Here are some examples:
- Meteorologists use barometers to forecast the weather. Generally, rising barometers mean better weather. A falling barometer means bad weather, like storms or rain.
- Altitude is measured by barometers (altimeters). Altitude readings are crucial for safe takeoffs, landings, and maintaining proper flight levels.
- Various scientific experiments use barometers to study atmospheric pressure. You can see how pressure changes with altitude or weather.
- The atmosphere is balanced against a column of liquid (usually mercury) or a flexible chamber in barometers.
Air pressure science
The sea-level pressure ranges from 27 inches to 31 inches of mercury, or 95 to 105 kPa for you metric types and air pressure can be measured with several types of barometers. Here are some of the most common types:
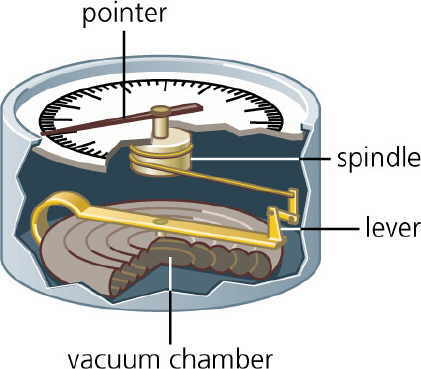
 Aneroid barometer movement
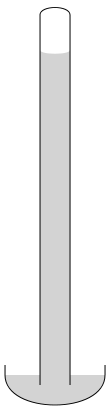
Aneroid barometer movement-A mercury barometer uses a glass tube filled with mercury at one end. A vacuum is created above the mercury in the tube by placing the open end in a container of mercury. When the air pressure changes, the mercury rises or falls inside the tube, providing a pressure measurement.
-Aneroid barometers use a small, flexible metal box that's sealed and has most of the air removed. A metal box expands or contracts when the air pressure changes, and this movement is amplified by levers and gears to measure the pressure.
-A digital barometer measures air pressure with electronic sensors and displays the results on a screen. Often used in weather stations and other applications where pressure needs to be monitored constantly.
-A barograph records changes in air pressure over time with a rotating drum and a pen. Typically, the drum is covered in paper, and the pen is attached to a lever that moves up and down as the pressure changes.
Interpreting the Air pressure measurements a barometer makes
Weather patterns and conditions can be affected by changes in air pressure. Here are some examples:
-A high-pressure system is where the air pressure is higher than the surrounding area. A high-pressure system usually means clear skies and calm weather, since the high-pressure zone prevents clouds from forming, more sun, higher temperatures, and fewer winds.
-A low-pressure system is where the air pressure is lower than the surrounding area. Because low-pressure zones allow warm, moist air to rise and cool, they usually cause cloudy, rainy, stormy weather, or snow... and wind power.
-Differences in air pressure between adjacent regions can cause pressure gradients, which can cause wind to move from high-pressure zones to low-pressure zones. Pressure gradients can affect wind strength and direction.
-Fronts are boundaries between air masses with contrasting characteristics, like temperature, humidity, and pressure. Precipitation, thunderstorms, and other severe weather can result when a cold front collides with a warm front. Along fronts is where you usually find thunderstorms, precipitation, or other severe weather, such as when a cold front collides with a warm front.
I won't even mention barometric pressure headaches and arthritis. You might not be able to rely on these broad (synoptic) generalizations if you live near big hills. Other features, called mesoscale (smaller than synoptic) patterns, can mess with prevailing conditions.
Now, what do we use to measure the pressure?
Types of barometer makes
Different types of barometers make different measurements. We have more fundamental differences than just digital barometers, stationary barometers, and handheld barometers.
Types of barometers: There are several types of barometers, each with a different application. Here's another perspective on these designs:
- Mercury Barometers: These are mercury tubes inverted in mercury reservoirs. The height of the mercury column changes with air pressure. Air pressure pushes more mercury into the tube, raising the column. When air pressure drops, mercury levels drop. Mercury barometers are perfect for scientific research and meteorological stations because they're so accurate. Weather stations monitor atmospheric pressure.
- An aneroid barometer uses a small, flexible metal box called an aneroid cell. This cell expands or contracts as air pressure changes. These movements are mechanically amplified on dials. Altimeters are used in homes, ships, and airplanes because they're portable. Mountaineers and hikers can use it to measure altitude and predict weather.
- Digital barometers use electronic sensors to measure air pressure. Pressure sensors convert pressure changes into digital readings. They're in modern weather stations and portable devices. Modern weather stations, smartphones, and portable weather devices have digital barometers that show real-time pressure. Hikers and outdoor enthusiasts use digital barometers to measure altitude.
What is the height above sea level?
Nearly all barometer makes display the pressure and can be adjusted for altitude, your position on elevation maps. Why? Because Denver, for example, is a mile in the air, so the atmospheric pressure there is ALWAYS lower than Los Angeles.
Anyhow, it gives you a reading of the pressure caused by the current weather system AS IF you were at sea level.
In most cases, scientific barometers are electronic, such as those used in environmental data logging projects.
There are two gold electrodes configured as a capacitor inside a vacuum, and pressure causes the capsule to deform, causing a change in capacitance that can be measured and converted into units of pressure.
There are other types of barometers that use simpler principles and generally respond to changes in air pressure in a container without any air inside. For instance, take a look at one of those glass water barometers.
Pilots use these kinds of barometers shown here, called altimeters, to determine the altitude of their aircraft.
Barometers (such as the barographs noted above) are also used to note pressure tendency. How much has it changed over the last three hours, up, down, or stayed the same.
#2
Search this site for more information now.
Barometer pictures and science gifts:
You can find pictures of barometers on US or Canadian eBay or on a retail web page - including electronic, aneroid and liquid-filled models. Also, Wikipedia has photos and info.
See the StuffInTheAir homepage to learn more about
air and the weather.
People's interest in barometric pressure depends on their specific needs, activities, health concerns, or personal curiosity. Having a good understanding of barometric pressure can help you understand weather conditions, health impacts, and how the atmosphere works.
Go back from Barometer Makes to the Weather Equipment web page.
What are the different types of barometers and how do they measure air pressure?
The barometer is a useful tool for measuring air pressure. A variety of designs are available, including digital, aneroid, and liquid in glass.
Do you have concerns about air pollution in your area??
Perhaps modelling air pollution will provide the answers to your question.
That is what I do on a full-time basis. Find out if it is necessary for your project.
Have your Say...
on the StuffintheAir facebook page
Other topics listed in these guides:
The Stuff-in-the-Air Site Map
And,
Thank you to my research and writing assistants, ChatGPT and WordTune, as well as Wombo and others for the images.
GPT-4, OpenAI's large-scale language generation model (and others provided by Google and Meta), helped generate this text. As soon as draft language is generated, the author reviews, edits, and revises it to their own liking and is responsible for the content.



New! Comments
Do you like what you see here? Please let us know in the box below.